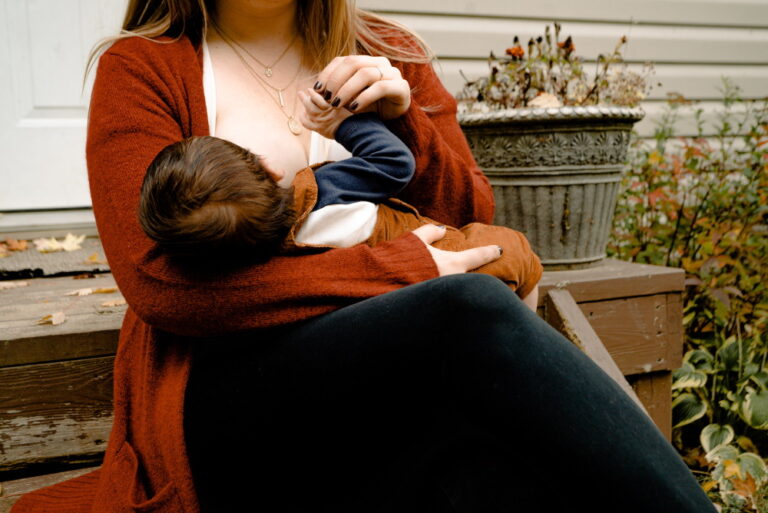
Breast milk supports your child’s healthy growth and development. Children who breastfeed complementary for six months achieve normal developmental milestones. Unfortunately, you can’t breastfeed your baby for years. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, children should breastfeed exclusively for six months. Mothers should then introduce solid foods alongside breastfeeding until their first birthday.
The decision to wean your baby from breast milk is personal. While some women begin immediately after six months to resume work, others wait until their babies grow into toddlers. Children are also different and tolerate weaning differently. Below are a few things new mothers should know when weaning their babies.
Switching to a Cup or Bottle
You should begin weaning your baby gradually. For starters, you can start feeding the baby using a cup or feeding bottle once daily. Over time, you can introduce more cup/bottle feeding sessions during the day and make breastfeeding less often. However, you should choose the best bottles for breastfed babies to avoid rejection.
It is easier to start by replacing daytime feeding, before naptime, and early morning feeding. Most babies find it difficult to give up on nighttime breastfeeding. You can save that for last. You can wean babies over six months old by skipping directly to cups and bottles.
Types of Weaning
There are several ways of weaning your baby from breastfeeding. You should choose an appropriate type based on your schedule and the baby’s reaction:
- Baby-led weaning – The baby can sometimes introduce weaning themselves. Young infants rarely start weaning themselves until after their first birthday. Signs of baby-led weaning include less frequent breastfeeding and, for short periods, if they can sit without support, doubled weight, mouthing hands and toys, and increased interest in solid foods.
- Gradual weaning – A slow weaning process that spreads over weeks or several months
- Partial weaning – A great alternative for mothers who can’t breastfeed exclusively
- Sudden weaning – Abruptly ending breastfeeding
- Temporary weaning – When breastfeeding is stopped for a period and then restarted. It often occurs if the mother or child develops health issues or needs surgery.
Babies who are weaned from the breast before one year should be fed on infant formula or pumped breast milk. Children can digest whole milk without complications after their first birthday.
When Should You Delay Weaning?
You should delay weaning your baby if:
- Your child isn’t feeling well – You should postpone weaning if your child is teething or feeling sick and if you are not feeling well. You should be in good health to handle this transition.
- You are worried about potential allergens – Weaning should also be delayed due to potential allergens. If the mother or father is allergic to some food items, weaning should be delayed until the child turns one. Exposing children to allergens while still breastfeeding increases the risk of developing allergies.
- Major changes – Don’t initiate weaning if a major event occurs or your family is undergoing a transitional period, such as moving to a new city or if you just hired a new caregiver.
Endnote
Weaning is a process, just like learning to breastfeed. It might take time for the mother and the baby to adapt. However, the baby needs to start feeding alternatively as milk production reduces.
Photo by Wendy Wei: https://www.pexels.com/photo/mother-breastfeeding-her-child-3074935/